A plastic extruder is an essential machine in the world of plastic processing. It is used to create a wide variety of plastic products by melting raw plastic material and forcing it through a mold or die to form a continuous shape. Extrusion is one of the most versatile and efficient manufacturing processes for producing plastic products such as pipes, sheets, films, profiles, and pellets. The versatility and cost-effectiveness of plastic extrusion have made it a staple in industries ranging from packaging to automotive, construction, and healthcare.
This article will explore the functionality, components, and types of plastic extruders, as well as the process and applications of plastic extrusion.
1. The Basic Concept of Plastic Extrusion
Plastic extrusion is a continuous process in which raw plastic material, typically in the form of pellets or granules, is melted and forced through a die to form a specific shape. The extruder performs three key functions during this process: feeding, melting, and shaping.
The basic structure of a plastic extruder includes a hopper, barrel, screw, heater, and die. The raw plastic material is fed into the hopper, where it is then transported into the barrel by the rotating screw. As the material moves through the barrel, it is heated by heaters along the barrel, causing the plastic to melt. Once the plastic reaches a molten state, it is forced through the die, which shapes the material into the desired form.
The result is a continuous extrusion of plastic that can be cut, cooled, and processed further to create the final product.
2. The Key Components of a Plastic Extruder
2.1. Hopper
The hopper is the starting point of the extrusion process. It is a funnel-shaped container where raw plastic material is loaded into the extruder. The hopper ensures that the material is fed consistently and evenly into the barrel. It may also include a vibrating mechanism to help prevent clogging and ensure uniform flow of material.
2.2. Barrel
The barrel is the cylindrical housing in which the screw rotates. The barrel is typically heated by external heaters to ensure that the plastic inside melts uniformly as it moves through the extruder. The temperature of the barrel is carefully controlled to achieve the desired melting point for the specific type of plastic being used.
2.3. Screw
The screw is a long, helical rod that rotates inside the barrel. It plays a vital role in transporting, mixing, and melting the plastic material. The screw is designed to move the material along the barrel, applying mechanical energy to the plastic to help it melt and homogenize. Depending on the type of extruder, the screw may have multiple sections, each serving a different function (e.g., feeding, compression, and metering).
2.4. Heaters
Heaters are mounted along the barrel to control the temperature of the plastic material as it moves through the extruder. They are critical to ensuring that the plastic melts at the right temperature for effective processing. The heaters are typically controlled by a temperature regulation system to maintain the proper heat profile.
2.5. Die
The die is the final component of the extruder and is responsible for shaping the molten plastic into its desired form. The die is typically made of metal and can be customized to create a wide variety of shapes, including pipes, sheets, films, profiles, and more. The shape of the die determines the final product's dimensions and surface texture.
2.6. Cooling System
Once the plastic material has been extruded through the die, it needs to be cooled quickly to solidify and retain its shape. Cooling can be achieved through a combination of air cooling, water cooling, or both, depending on the material and the product being produced.
3. How Does a Plastic Extruder Work?
The plastic extrusion process involves several stages: feeding, melting, extrusion, shaping, and cooling. Understanding how these stages work together helps to clarify the overall function of a plastic extruder.
3.1. Feeding the Raw Material
The process begins by feeding raw plastic material into the hopper. The material is typically in the form of pellets, granules, or powder. As the plastic material enters the hopper, it is gravity-fed into the barrel, where it is picked up by the rotating screw.
3.2. Melting the Plastic
Once inside the barrel, the plastic material is transported through the screw, which applies both mechanical energy and heat. The screw moves the material toward the die while heating it in the process. The heaters along the barrel are responsible for raising the temperature of the plastic to its melting point. The screw's design ensures that the material is mixed thoroughly to achieve a uniform molten consistency.
3.3. Extrusion and Shaping
Once the plastic reaches its molten state, it is forced through the die at the end of the extruder. The die has a specific shape or profile that determines the final shape of the extruded product. The pressure applied by the screw and the temperature of the material ensure that the plastic flows smoothly and fills the die completely.
3.4. Cooling and Solidification
After the molten plastic exits the die, it needs to cool down and solidify to retain its shape. This is typically done using a cooling system that sprays or immerses the extruded material in water or uses air cooling. The cooling time is carefully controlled to ensure that the plastic solidifies without any warping or defects.
4. Types of Plastic Extruders
There are several different types of plastic extruders, each suited to different applications and materials. The most common types of extruders are:
4.1. Single-Screw Extruder
The single-screw extruder is the most basic and widely used type of extruder. It uses a single, rotating screw to move the material through the barrel and melt it. Single-screw extruders are ideal for processing simple materials, such as thermoplastics, and are commonly used in the production of pipes, sheets, and films.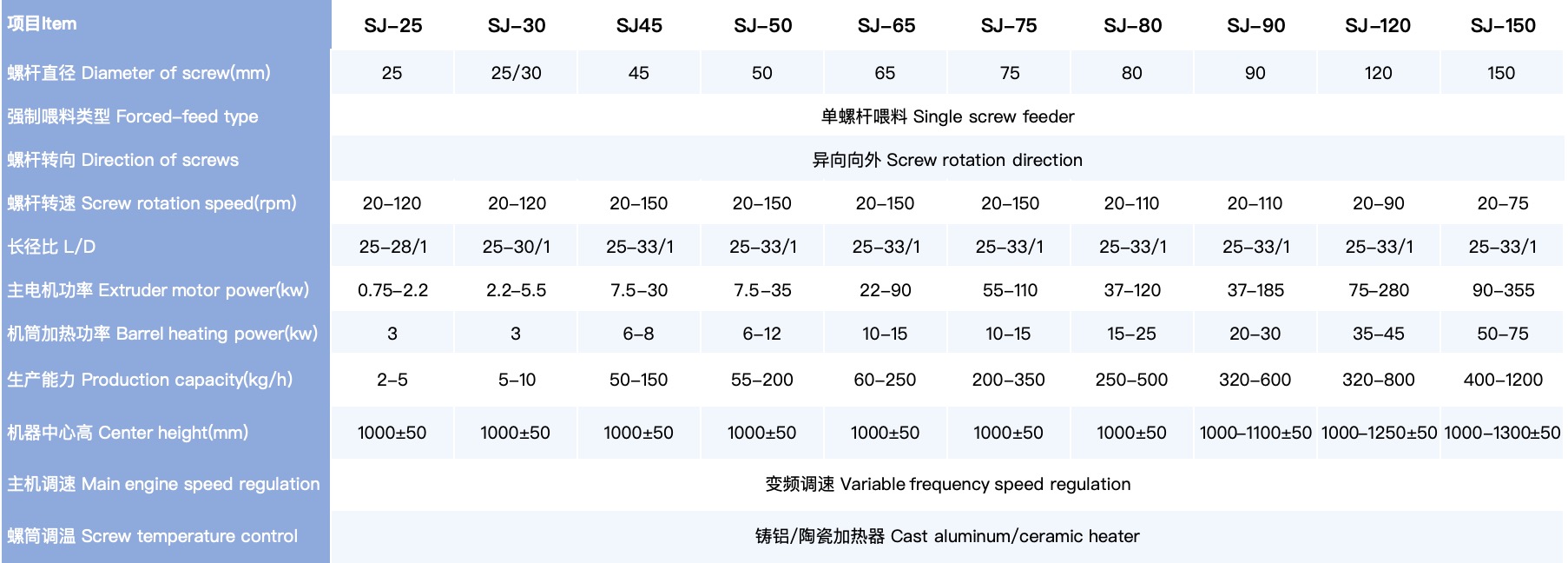
4.2. Twin-Screw Extruder
The twin-screw extruder uses two intermeshing screws that rotate in opposite directions. This design provides better mixing and processing capabilities, making it suitable for more complex materials, such as those with additives, fillers, or composite materials. Twin-screw extruders are often used in high-performance applications, such as compounding, masterbatch production, and food processing.
4.3. Co-Rotating Twin-Screw Extruder
A co-rotating twin-screw extruder features two screws that rotate in the same direction, allowing for more efficient material conveying and mixing. This type of extruder is particularly useful for processing high-viscosity materials and polymers with high molecular weights. It is often used for compounding and high-performance polymer processing.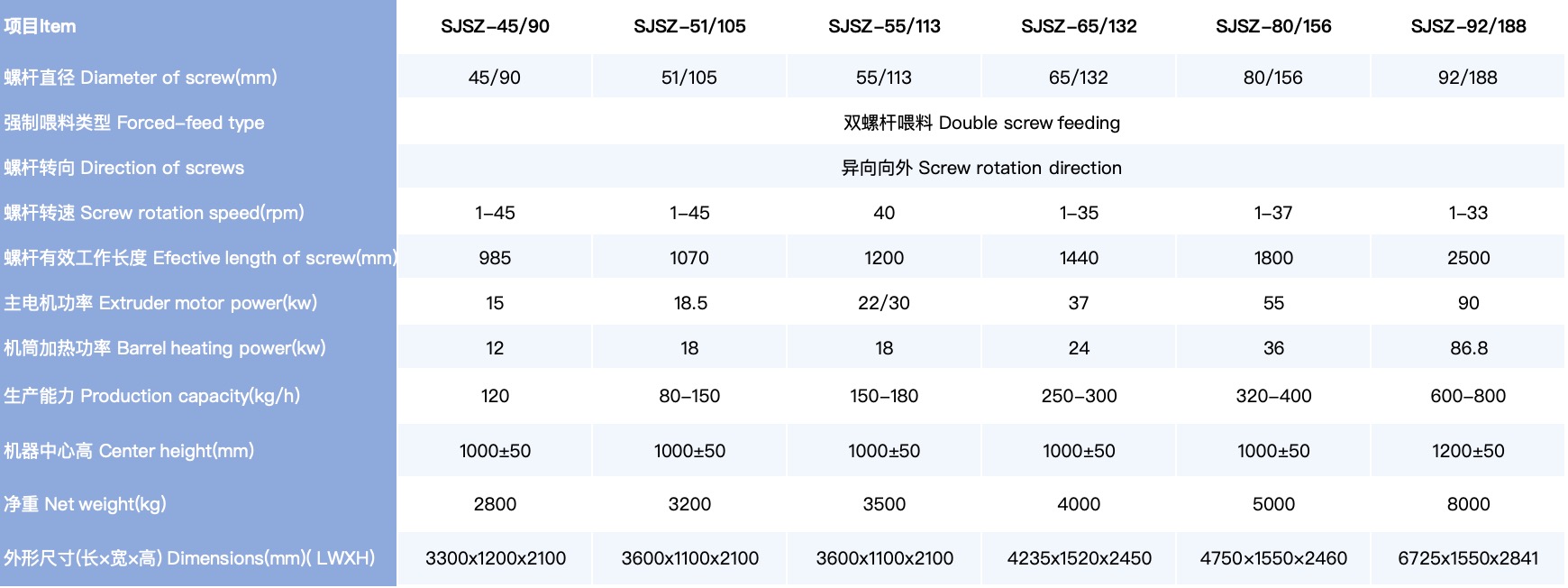
4.4. Planetary Roller Extruder
The planetary roller extruder features a rotating central screw surrounded by multiple smaller rollers. This type of extruder is commonly used for producing products with intricate shapes, such as profiles, or for mixing high-viscosity materials. It is frequently used in the production of rubber compounds, food products, and high-performance polymers.
5. Applications of Plastic Extruders
Plastic extruders are used in a wide range of industries to produce various products. Some of the key applications of plastic extrusion include:
5.1. Pipe and Profile Production
One of the most common applications of plastic extrusion is the production of pipes and profiles. Extruders are used to produce pipes for water, gas, and sewage systems, as well as various types of profiles for windows, doors, and construction applications. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polyethylene (PE), and polypropylene (PPR) are commonly used materials in this application.
5.2. Film and Sheet Production
Plastic extruders are also used to produce films and sheets used in packaging, medical applications, and construction. These films are often made from materials like polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and polystyrene (PS) and are used for everything from food packaging to agricultural films and medical products.
5.3. Wire and Cable Insulation
Extruders are essential in the production of insulated wires and cables. Plastics such as PVC, polyethylene, and cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) are extruded around copper or aluminum wires to create insulation that protects the wire and ensures safety in electrical and telecommunications applications.
5.4. Medical and Pharmaceutical Applications
In the medical field, extruders are used to create products such as tubing, catheters, and drug delivery devices. The precision of the extrusion process allows for the creation of medical products with high standards of quality and consistency, which is critical in applications where performance and safety are paramount.
5.5. Automotive and Aerospace Components
Plastic extruders are used in the production of automotive and aerospace parts, including seals, gaskets, and interior components. High-performance materials are often used in these applications to meet stringent regulatory and performance standards.
6. Conclusion
A plastic extruder is a powerful and versatile machine used to process a wide range of materials into shapes and products that are used in numerous industries. By controlling key factors such as temperature, pressure, and screw speed, plastic extruders can create everything from simple pipes to complex medical devices with precision and consistency. The continued advancement of plastic extrusion technology allows manufacturers to produce a broader variety of products more efficiently and cost-effectively, contributing to innovations across many industries. Understanding the function and capabilities of plastic extruders is key to optimizing the extrusion process and ensuring high-quality, reliable results.


























